Carbon Credit Exchanges
Carbon credit exchanges are an emerging industry that allows buyers and sellers of carbon credits to trade in real time. This is a great way to make use of carbon offsets and help reduce carbon emissions. However, it can be confusing to figure out what these exchanges do and how they work.
The main purpose of these carbon credit exchange markets is to help companies and individuals offset their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The market also provides support for government efforts to fight climate change. Some of the largest buyers of these credits include airlines, tech companies, and oil and gas majors. Several countries have implemented this type of system.
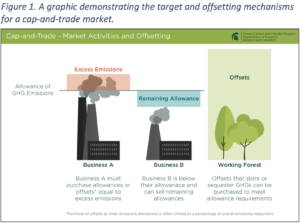
A typical carbon market is divided into two basic types: a voluntary market and a compliance market. Both of these markets have their own unique sets of requirements. For example, a company that exceeds the emissions cap on a project may be forced to purchase extra credits. There are also different standards for certifying these credits.
What Does Carbon Credit Exchanges Do and How Do They Work?
The voluntary market is driven by the desire to meet international climate goals. As such, many industry sectors are now setting net-zero targets. In addition, the number of entities acquiring carbon credits has risen, as more companies look for ways to hedge their financial risks as the global energy transition moves to renewables.
Among the most important functions of a carbon credit exchange is to help establish a price. Credits must be proven to produce a reduction in CO2 and to ensure that their owners are the right people to benefit from them. Companies can choose to purchase credits directly from the developer of the project or from a middleman.
It is often the case that larger industrial projects can generate significant volumes of credits, making it easy for them to buy large amounts. Smaller-scale projects typically have more difficulty proving that they will reduce GHGs. Still, the price of these credits is heavily influenced by the annual price of carbon.
The best carbon exchanges will also provide a variety of tools for companies and organizations. One exchange, the AirCarbon Exchange, offers a variety of options for the aviation industry, including a digital trading platform, an auditing and verification system, and a registry system.
Using this technology, ACX is able to create a securitized carbon credit market that takes advantage of the speed and efficiency of blockchain technology. These exchanges are designed to provide a safe and secure method for both buyers and sellers of carbon to trade in real time.
The digital process could reduce issuance costs and accelerate cash flow for project developers. Creating an open and transparent credit marketplace could also improve the credibility of corporate offsets.
The market has been criticized for its lack of transparency. Because of the many intermediaries involved in the trade, it is difficult to determine whether money has been spent on good causes or not. Moreover, a lack of clarity in the pricing of these products creates a potential for money laundering.