Flex PCBs
A flex circuit board is a printed circuit board that can be bended or twisted. It is a great option for electronic devices that are designed to be used in a variety of shapes and sizes. This allows them to adapt to a wide range of applications that would be difficult or impossible for rigid circuit boards to accommodate. Moreover, they are much thinner and lighter, which can help reduce the overall weight of an application’s motherboard. Additionally, they are able to take up less space than conventional PCBs, which can also help to improve the design’s thermal management system.
In addition to its flexibility, a flex pcbs can withstand high temperatures and harsh working environments. These factors can be particularly important for devices that will be exposed to extreme conditions, such as vibrations and shocks, which may otherwise cause them to fail. These characteristics have also made them popular in a wide range of industries and applications, from medical equipment to military and aerospace electronics.
Whether your project requires a rigid, flex or hybrid PCB, the type of material and manufacturing process will make a big difference in how it functions in the field. The choice of materials is also important for ensuring the durability and longevity of your product. This is because it will affect how well your flex circuit can withstand different environmental factors, such as heat and moisture.
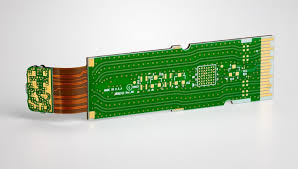
What Are Flex PCBs?
The most common substrates for flex circuits are PI or PET films, as well as thin flexible epoxy and glass-fiber cores. These substrates are then covered with a specialized coverlay, similar to the solder mask on rigid PCBs. This layer encapsulates the outer surface of the conductors and protects them from corrosion, damage, and other elements that may harm them in the field.
Another key factor in a flex circuit’s ability to withstand vibrations and shocks is its construction. A flex circuit’s copper foil is typically annealed, which increases its strength and resistance to heat. It is also insulated with a polyimide or other insulating film, which prevents the conductors from heating up too quickly and damaging the internal layers.
Finally, it is important to note that a flex circuit’s design can also impact its ability to endure bending and twisting. For example, it is best to avoid using solid copper in areas that are expected to be bended, as this can lead to cracking and weaken the structural integrity of the flex circuit. Instead, a hatched copper or patterned copper could be used, which will provide better mechanical performance and allow the circuit to flex more easily without damaging it.
In the end, it’s important to understand that a flex circuit board will likely cost more than a traditional rigid PCB because it requires additional fabrication steps. However, it’s still a highly-effective solution for many projects that require greater adaptability and performance than standard rigid PCBs can offer. Before you order your flex PCBs, be sure to check out our detailed calculator to find out how much your project will cost. You can also contact us if you have any questions or need help finding the right type of flex PCB for your design.